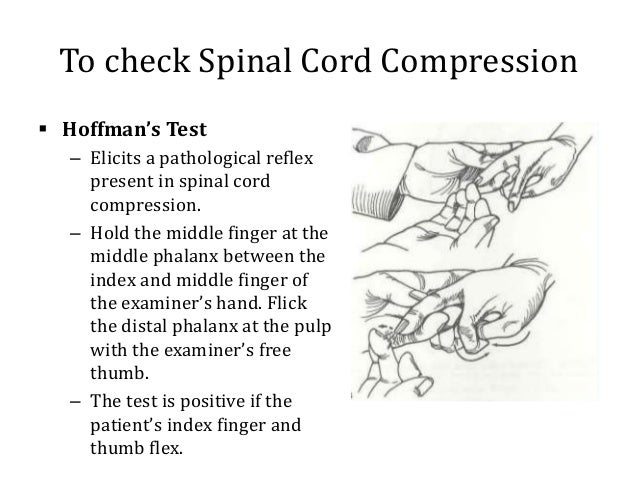
Hoffmann sign clinical correlation of neurological imaging findings in the cervical spine and brain There were 80 patients in the negative Hoffmann sign or control group Twentyone (27%) of them had severe cervical cord compression and/or myelomalacia Twentythree of these control patients underwent neurological imaging of the brain, and 2 (8%) had positive findings Hoffmann sign was found to have 59% sensitivity, 49% specificity, 35% Hoffmann's reflex ( hoffmann's sign , sometimes simply hoffmann's , also finger flexor reflex ) 1 is a neurological examination finding elicited by a reflex test which can help verify the presence or Hoffmann reflex finger flexor reflex, brain and spine a k mourya Examiner cradles patient's relaxed hand 2

Medicosnotes Com What Is Hoffman Reflex A Complete Guide
Positive hoffman sign neurology
Positive hoffman sign neurology-NEUROLOGICAL SIGN Jon Stone1 and Michael Sharpe2 Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Western General Hospital, Crewe Road, Edinburgh Email jstone@skulldcnedacuk;The presence of Hoffmann sign on both sides strongly suggests the presence of spinal cord compression in the cervical spine This is very helpful information when assessing patients with very few other objective findings However, the test is not foolproof because patients who don't have cervical myelopathy can have a positive Hoffmann sign




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Orthopaedia
Enroll in our online course http//bitly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP📱 iPhone/iPad https//googl/eUuF7w🤖 Android https//googl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT BHoffmann sign was observed in 68% of patients operated on for cervical spondylotic myelopathy In 11 patients presenting with lumbar symptoms but no myelopathy, a bilateral Hoffman sign was associated with occult cervical spinal cord compression in 10 (91%) 2)It is an early sign of pyramidal diseaseThe Hoffmann's sign is observed in upper motor neuron lesion (UMNL) The upper motor neuron injury mean that there is damage to the spinal cord and/or brain Hoffmann Sign is considered as a Red Flag for Cervical Myelopathy The Hoffmann sign is a reliable way to test for early signs of cervical myelopathy
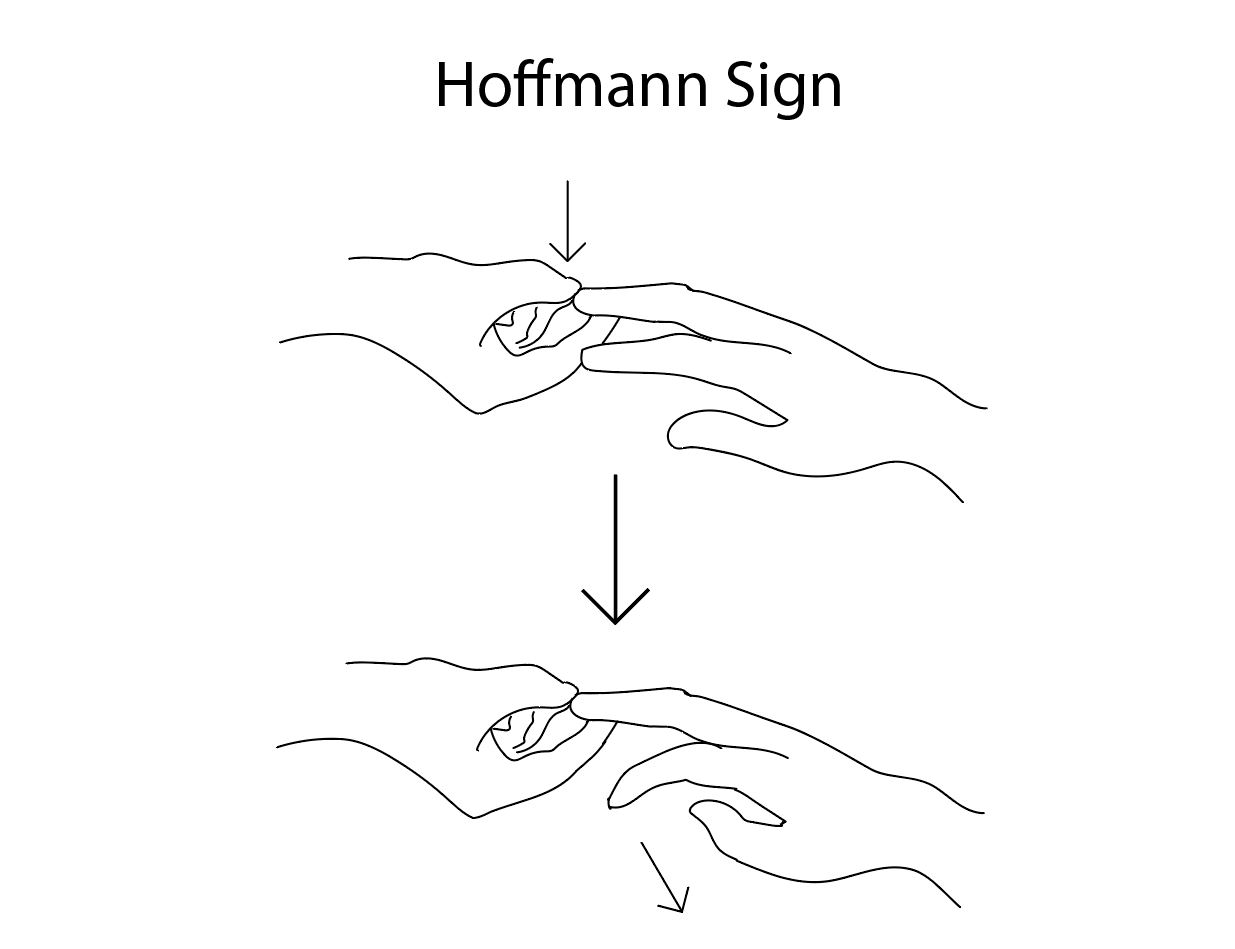
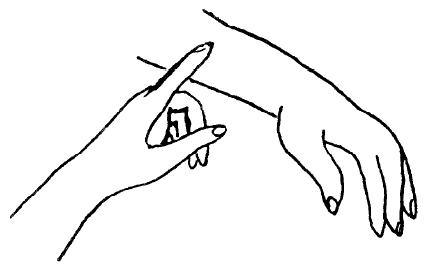
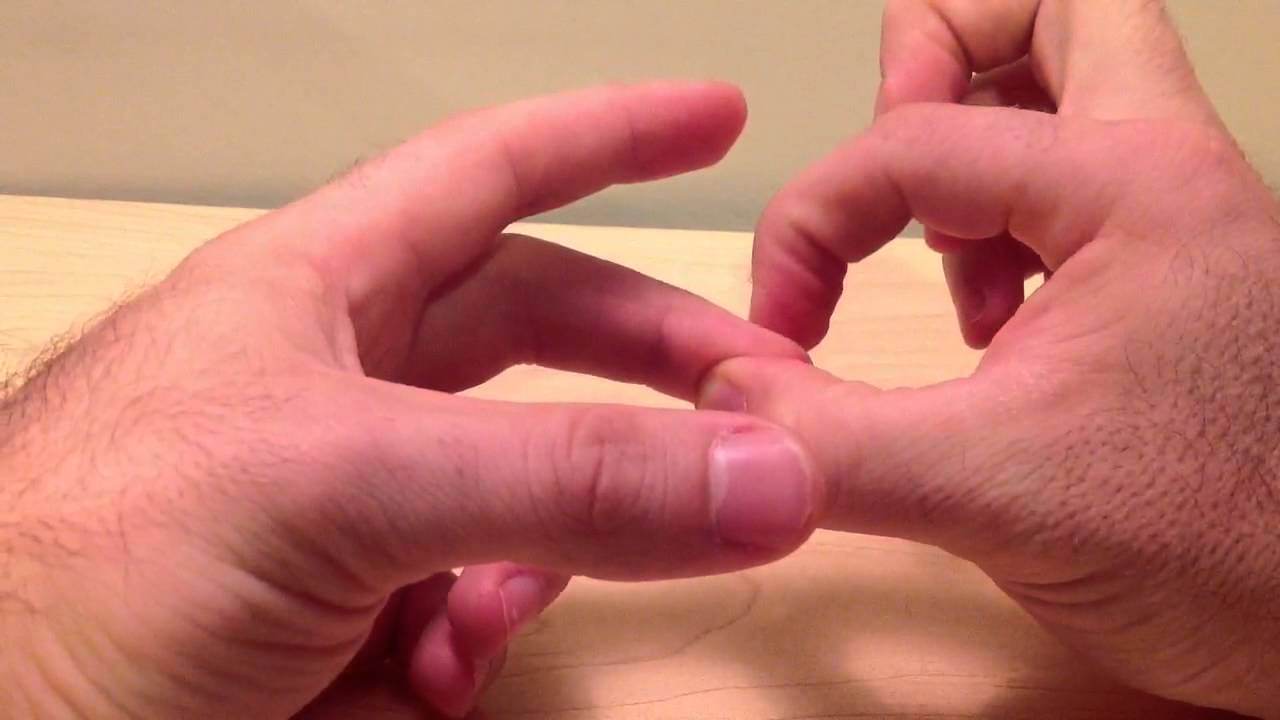
The Hoffman sign is an abnormal reflex response that consists of flexing the fingers of the hand when pressing the nail of the middle finger Although it is generally associated with pathologies such as pyramidal syndrome, it can occur in healthy people who have heightened reflexes (which is called hyperreflexia) Your neurological finger tapping reflex, also known as the Hoffman sign, is used to identify damage to the central nervous system and monitor recovery from brain injury This reflex is triggered by stimulated neurons triggering a cascade of voluntary skeletal muscle contractions known as evoked muscle accidents (EMCA)The German neurologist Johann Hoffman first postulated this sign It was described by his assistant Hans Curschmann in 1911 and has become a standard part of the common neurologic exam The Hoffman sign is an involuntary flexion movement of the thumb and or index finger when the examiner flicks the fingernail of the middle finger down
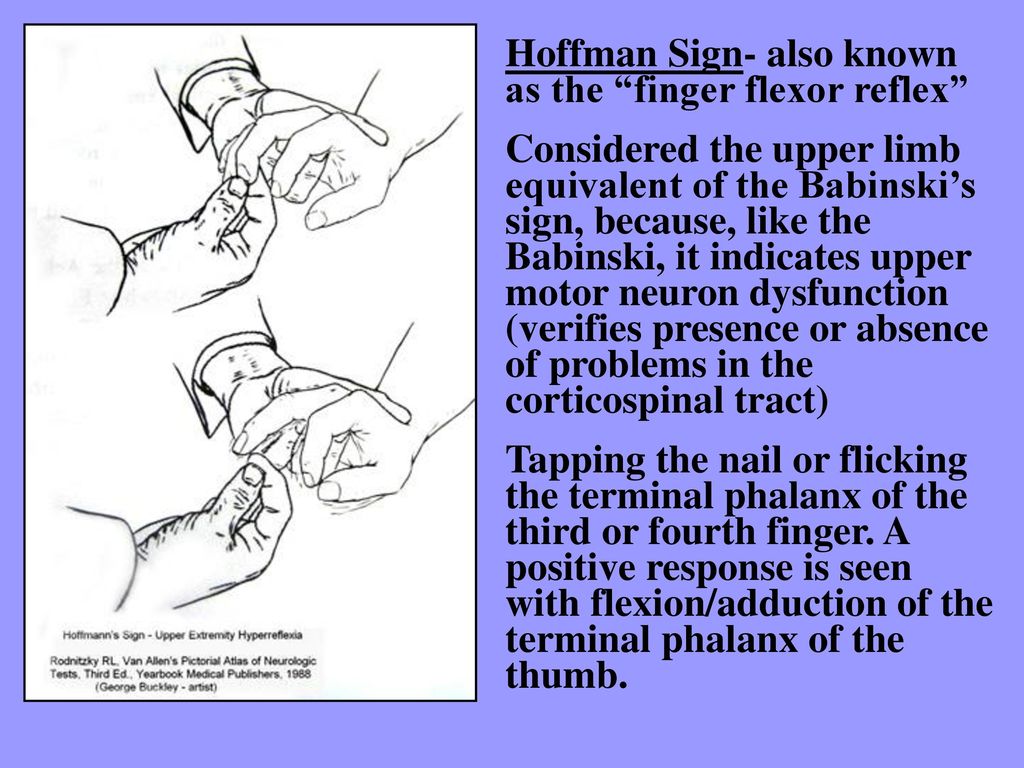
2 flexion of the terminal phalanx of the thumb and of the second and third phalanges of one or more of the fingers when the volar surface of the terminal phalanx of the fingers is flicked Synonym(s) digital reflex ,HOFFMAN CALIFORNIA FABRICS Obrero Drive Mission Viejo, CA RETAIL & SPECIALTY MANUFACTURERS (800) Fax (949) MANUFACTURERS The Hoffman sign Involuntary flexion of the thumb and/or index finger when the fingernail of the middle finger is flicked down Positive Hoffman sign Upper motor neuron lesion and corticospinal pathway dysfunction due to cervical cord compression Falsepositive 3% of the population have a positive Hoffman without cord compression or upper




Perfect Hoffman S Sign With Paul Marquis Pt Youtube




Hoffmann S Sign Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube
Is your question why the doctor2Department of Psychological M edicine, Royal Edinburgh Hospital, Morningside Park, EdinburghHoffmann sign were found to have neurological imaging of the brain (34 magnetic resonance images and 13 plain CT scans) for review Of these, 5 (10%) had positive




Neurological Examination Knowledge Amboss



Hoffmann Sign Article
Out of the five tests, the two that students have the most trouble with (and never see a positive sign) are the Hoffman's Test and Inverted Supinator Sign I find both of these to have high specificity values in my practice (which means if the test is positive, a high probability of an upper motor neuron disorder is present)NeuroLinguistic therapy assumes there is a connection between the mind's processes ("neuro"), language ("linguistic") and behavioral patterns learned Hoffman's Sign is just one possible indicator that not all might be well in your cerebral cortex Hoffman Sign Hoffman sign is a test that may reveal the presence of a lesion in the upper motor neuron in the spinal cord A positive sign occurs when there is a reflexive response in the thumb, to tapping the nail of the third or fourth finger




Pin On Neuroscience




Neurological Signs In Medicine
A positive Hoffman's sign may indicate that you have a neurological or nervous system condition that affects the cervical spine nerves or brainHoffman's sign is a neurological sign in the hand which is an indicator of problems in the spinal cord It is associated with a loss of grip The test for Hoffman's sign involves tapping the nail on the third orHoffman's sign or reflex is a test that doctors use to examine the reflexes of the upper extremities This test is a quick, equipmentfree way to test for the possible existence of spinal cord compression from a lesion on the spinal cord or another underlying nerve condition The sign takes its name from a German neurologist called Johann Hoffman



Paul Hoffmann Litfl Medical Eponym Library




Hoffmann S Reflex Operative Neurosurgery
Benjamin Hoffman, MD is a neurologist practicing neurology in Atlanta He has been with Wellstar since 18Hoffman sign can be present in healthy people As long as you don't have weakness or atrophy, you are basically fine Motorneurone disease is absolutely impossible without weakness or atrophy 1 level 1 Blagoonga 1y I also had brisk reflexes on kneesConclusion Hoffmann sign has too low a positive predictive value to be relied upon as a standalone physical examination fi nding and is not a reliable screening tool for solely predicting the presence of cervical spinal cord compression or brain pathology Key words Hoffmann sign , clinical correlation , neurological




Hoffmann S Sign Or Reflex Upper Motor Neuron Lesion Youtube




Pdf Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign Semantic Scholar
A positive Hoffman response is indicative of an upper motor neuron lesion affecting the upper extremity in question Finally, test clonus if any of the reflexes appeared hyperactive Hold the relaxed lower leg in your hand, and sharply dorsiflex the foot and hold it dorsiflexedCervical spinal cord compression and the Hoffmann sign Iowa Orthopaedic Journal, 21, 4952 Hoffmann Sign Red Flag for Cervical Myelopathy (sf) Recuperado el 9 de abril de 17, de Eorthopod eorthopodcom Hoffman's sign (21 de enero de 08) Obtenido de Mult Sclerosis multsclerosisorg Hoffman's Sign (11 de abril de 12) A Clinical Correlation Research of the Hoffmann Sign and Neurological Imaging Findings in Cervical Spinal Cord Compression Cao J, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhao L, Wang W, Zhang M, Wang L World Neurosurg, 128e7e786, Cited by 0 articles




The Method Of Eliciting The Reflexes A Eliciting The Hoffman S Download Scientific Diagram




Functional Symptoms And Signs In Neurology Assessment And Diagnosis Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
Twitching or flexion displayed in the other fingers on the hand in response generally represents a positive Hoffmann's sign Neurology studies indicate that a positive sign usually indicates upper motor abnormalities caused by compression or irritation of the spinal column Under these circumstances, the nerve cells remain in a constant state of excitation known as tetanyHoffmann sign ( hof'mahn ), 1 in latent tetany mild mechanical stimulation of the trigeminal nerve causes severe pain;Twentythree of these control patients underwent neurological imaging of the brain, and 2 (8%) had positive findings Hoffmann sign was found to have 59% sensitivity, 49% specificity, 35% positive predictive value, and 72% negative predictive value for cervical cord compression For brain pathology, sensitivity was 71%, specificity 33%



Cervical Spine Arthur Jason De Luigi Do Ppt Download




Hoffmann S Sign Was Originally Described As Follows Grepmed
Hoffman DO PhD Neurology • Rochester, MN Neuromuscular Medicine, Neurophysiology Assistant Professor Join to view full profile Dr Hoffman is on Doximity As a Doximity member you'll join over a million verified healthcare professionals in a private, secure network Conclusion The Babiniski of the arm, that is, the upper extremity analogue of the plantar extensor response Singly or jointly, the reflexes of Hoffman and Tromner have evolved to form an integral part of the current, standard neurological examination When present bilaterally , Hoffman sign is usually an indication of hyperactive deep tendon The Hoffman sign is the result of the Hoffman test, which is used to test the fingers and thumb for symptoms of a central nervous system problem This could include spinal nerves



Hoffman S Sign Hand Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote




What Is Hoffman Sign Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote
"went to dr for clumsinessi had hyperreflexsirms jaw jerk present positive hoffman's sign babinski present & clonus neuro ordered mri ??" Answered by Dr Mark Fisher Dr ordered MRI What is your question?Hoffmann's sign is a test for pathological disorder in upper motor neuron reflex as seen in cervical myelopathy when the spinal cord in the cervical spine gets compressed and chances are that the patient will exhibit pathological reflexesThe test involves tapping the nail or flicking the terminal phalanx of the middle or ring finger A positive response is seen when terminal phalanx of the thumb flexes A positive Hoffman's reflex may indicate an upper motor neuron lesion or a pyramidal sign Hoffmann's reflex may be seen in the following conditions Multiple sclerosis ALS




Pdf Reliability And Repeatability Of The Hoffmann Sign Lance Goetz Academia Edu




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Guide To Diagnosis And Management American Board Of Family Medicine
Some authors indicate that e The Hoffman sign is more likely in patients with less severe neurological problems Apparently, the Hoffman sign can also be an indicator of multiple sclerosis It is observed when there have been injuries in the nerve motor or spinal cord in the part of the nerves that control the movements of the hands (like C5)Hoover's sign of leg paresis is one of two signs named for Charles Franklin Hoover It is a maneuver aimed to separate organic from nonorganic paresis of the leg The sign relies on the principle of synergistic contraction Description Involuntary extension of the "normal" leg occurs when flexing the contralateral leg against resistance The German neurologist Johann Hoffman first postulated this sign It was described by his assistant Hans Curschmann in 1911 and has become a standard part of the common neurologic exam1 The Hoffman sign is an involuntary flexion movement of the thumb and or index finger when the examiner flicks the fingernail of the middle finger down




A Positive Hoffman S Reflex Orthopedic Therapy




Hoffman Sign Test Results And More
Dr Michael W Hoffmann is a neurologist in Winter Garden, Florida He received his medical degree from University of the Witwatersrand and has been in practice for more than yearsNeurosurgeons may also be known by the following names neurological surgeon, brain surgeon, spine surgery specialist, and spinal cord surgeon There are 19 specialists practicing Neurosurgery in Hoffman Estates, IL with an overall average rating of 43 stars The Hoffmann reflex is finger flexor response is demonstrated by a sudden flexing of the thumb and/or index finger, and can be a sign of MS



Hoffmann S Reflex Neurologyneeds Com




Neurological Signs In Medicine
What is Hoffmann's sign or Hoffmann's Reflex? Findings Abnormal (Positive Hoffman Sign) Involuntary flexion and adduction (opposition) of the thumb Other fingers may also flex (eg index finger) IV Causes Abnormal Reflex Normal finding in 3% of US population (typically present bilaterally in these patients) Upper Motor Neuron Lesion ( Corticospinal tract)Hoffman Sign Aka Hoffman Sign, Hoffman Reflex, Hoffman's Reflex Technique Patient pronates hand with fingers extended and relaxed Examiner holds the patient's pronated hand, and supports the middle finger below the DIP joint Examiner quickly presses or flicks down on the Fingernail region of the middle finger




Hoffman S Sign Positive Youtube



Neurology
In patients surgically treated for cervical myelopathy, the Hoffmann sign is more prevalent and more likely to be seen in individuals with During a standard neurological exam, the Hoffman sign is common, and a positive sign can aid in the diagnosis However, a 18 systematic review, with level 1 evidence, on the utility of the Hoffman sign for the diagnosis of degenerative cervical myelopathy found insufficient data to support the use of the exam alone to confirm or refute a




Pep Test 3 Neuro Eval Flashcards Quizlet



Approach To Neck Pain




The Technique Used To Evoke The Hoffmann Reflex In Each Photograph Download Scientific Diagram



Hoffman Sign



Neck Upper Extremity Spine Exam Spine Orthobullets




Upper Limb Neurological Examination Inspection Muscle Tone Muscle




Perfect Hoffman S Sign With Paul Marquis Pt Youtube




Occupational Therapy Assessment In Neuro Rehab By Theraspot Medium



2



1



The Diagnostic Quandary Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Negative Hirayama Disease A Case Report Journal Of Medical Case Reports Full Text



Oip Com




Pyramidal Signs Wikipedia




Hoffman S Sign Hand Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote




Johann Hoffmann Litfl Medical Eponym Library




Positive Hoffmans Sign And Inverted Supinator Sign Cervicogenic Dizziness




Pdf Clinical Sign Revisited Hoffman S Sign




Nerve Roots Reflexes Special Tests Landmarks Flashcards Quizlet



Simple Care Plan Lloyd Bennett Nursing Diagnosis Objective Goals Short And Long Term Relate To Studocu




Acute Peripheral Neurologic Lesions Neurology Tintinalli S Emergency Medicine Just The Facts 3ed




The Precise Neurological Exam




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean




Hoffmann S Sign Or Reflex Upper Motor Neuron Lesion Youtube




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Orthopaedia




Ms Signs Vs Symptoms What Is The Hoffmann Reflex
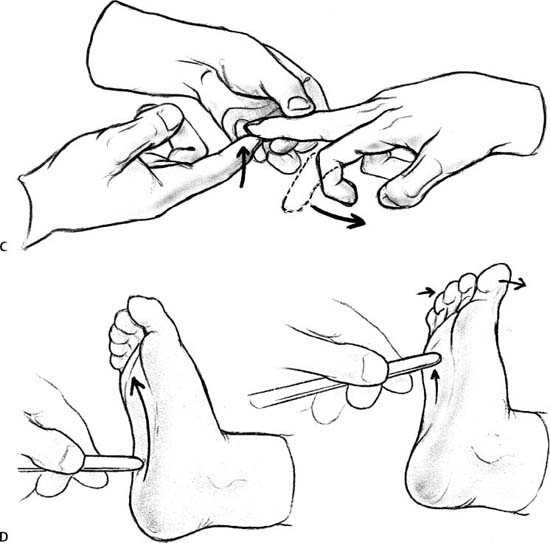



History And Physical Examination Neupsy Key



2




Continuum Lifelong Learning In Neurology Bonus Key Point 2 From The Article Spondylotic And Other Structural Myelopathies By Dr Shamik Bhattacharyya Available To Subscribers At T Co Rxdmjdp1ij Neurology Meded Neurotwitter




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




Performing A Neurological Examination On Patients With Musculoskeletal Extremity Symptoms Part I Clinical Reasoning And Statistical Utility Athletic Training Sports Health Care




Eliciting The Hoffman Reflex Video Ditch Doc Em




Hoffman S Sign Performed In Slow Motion Youtube




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08 Journals




Functional Neurological Disorders In Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery Illustrative Case In Journal Of Neurosurgery Case Lessons Volume 1 Issue 2 21 Journals




What Is Hoffman Sign Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote




Medicosnotes Com What Is Hoffman Reflex A Complete Guide
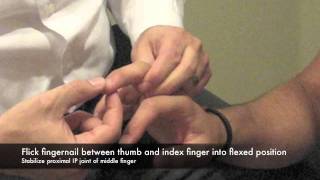



Hoffmann S Sign Physiopedia
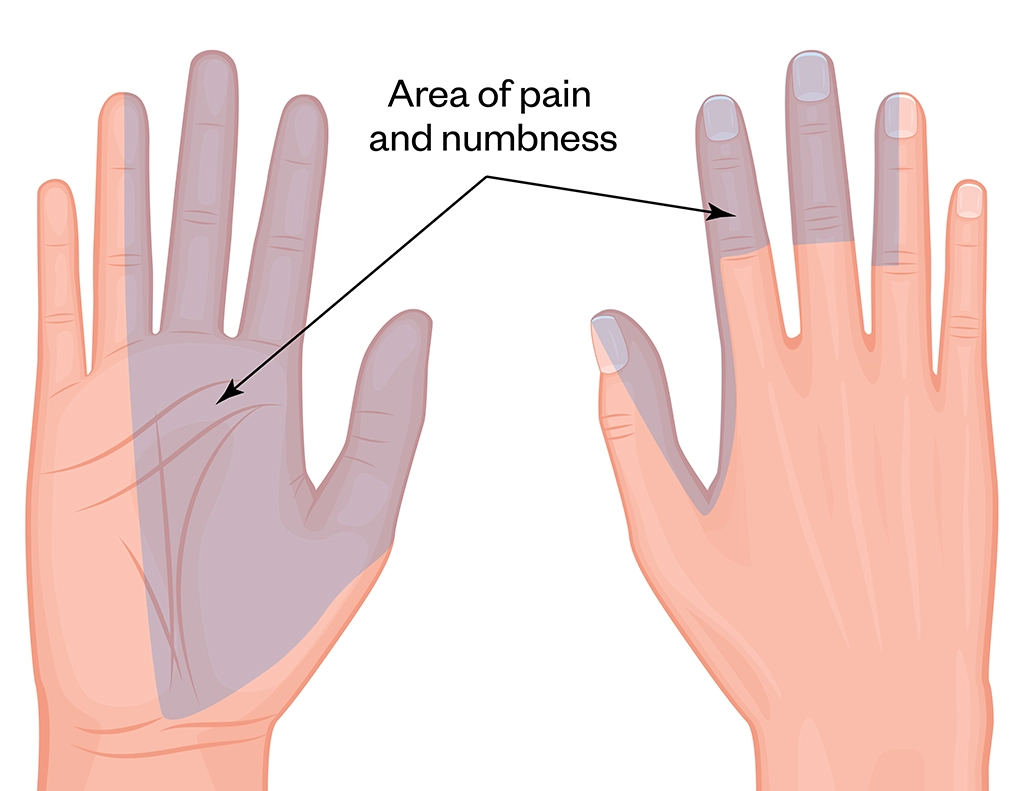



Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Identification And Management The Pharmaceutical Journal



Pyramidal Voluntary Motor System Ppt Download




Pdf Determination Of Sensitivity And Specificity Of Hoffmann S Sign In The Diagnosis Of Patients With Compressive Cervical Myelopathy




Neurological Signs In Medicine




Performing A Neurological Examination On Patients With Musculoskeletal Extremity Symptoms Part I Clinical Reasoning And Statistical Utility Athletic Training Sports Health Care



Back To Basics A Spine Disorder Photo Quiz




What Is Hoffman Sign Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote




Neck Pain Diagnosis And Management



What Is The Babinski Reflex
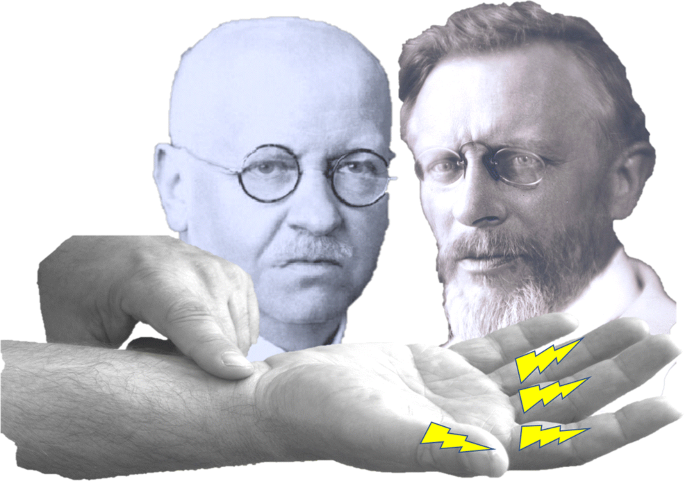




Paul Hoffmann 14 1962 Ad And Jules Tinel 1879 1952 Ad And Their Legacy To Neuroscience The Hoffmann Tinel Sign Springerlink




The Method Of Eliciting The Reflexes A Eliciting The Hoffman S Download Scientific Diagram
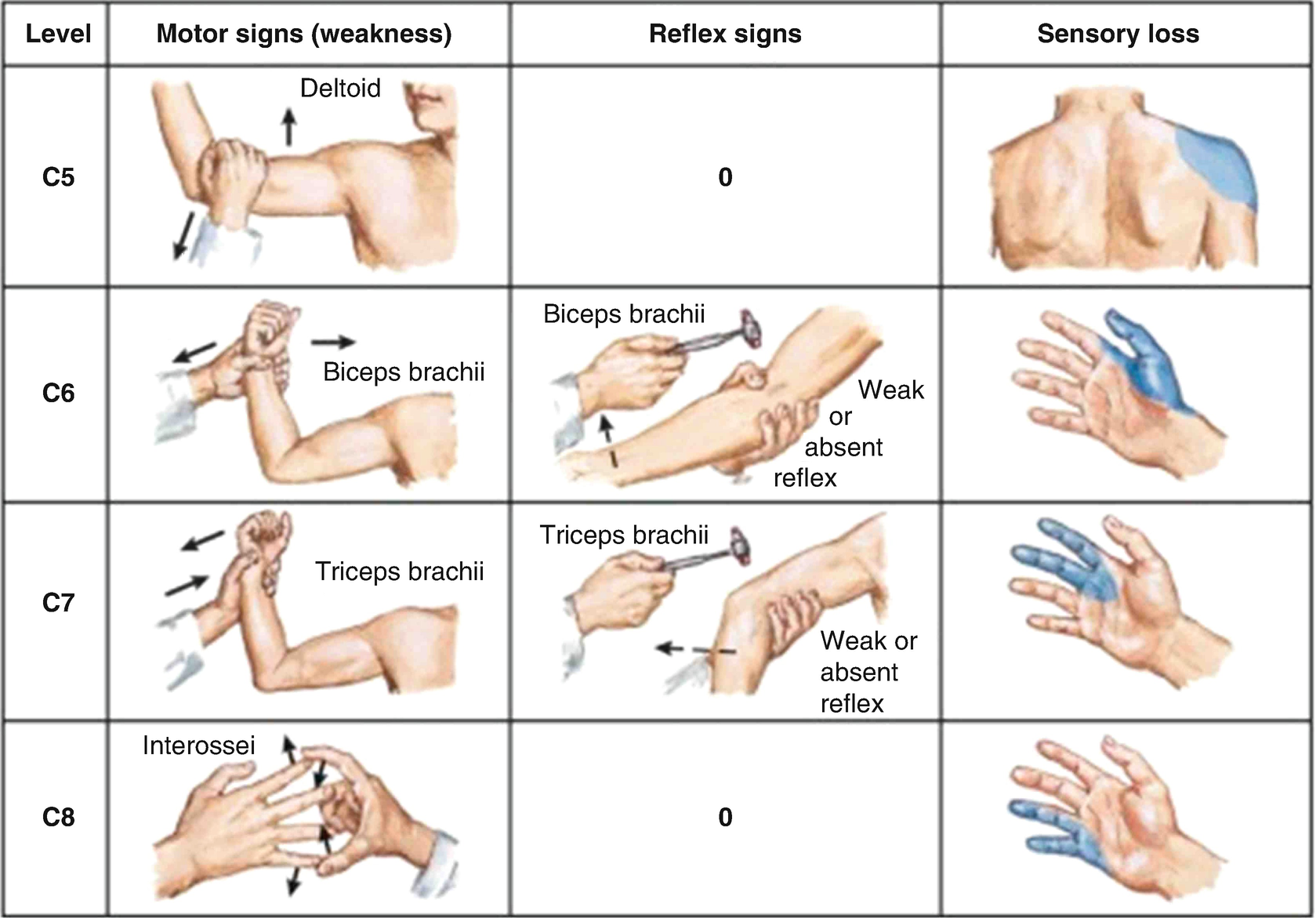



Fundamentals Of Cervical Neurological Exam Springerlink




A Clinical Correlation Research Of The Hoffmann Sign And Neurological Imaging Findings In Cervical Spinal Cord Compression Sciencedirect




Neurological Signs In Medicine




25 Hand Exercises For Stroke Patients Stroke Recovery Home Exercises



Ns Neurospine




Hoffmann S Sign Test Myelopathy Multiple Sclerosis




Neurological Assessment Physiopedia




Hoffmann S Sign Test Myelopathy Multiple Sclerosis




Approaching Neck Pain Mcp Ipa Lbp Task Force Ppt Download




Neurological Signs In Medicine




Positive Hoffmans Sign And Inverted Supinator Sign Cervicogenic Dizziness




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean




Videos Archives Saebo



1




Nexus Criteria For C Spine Injury Peripheral Brain



The Diagnostic Quandary Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Negative Hirayama Disease A Case Report Journal Of Medical Case Reports Full Text




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Tinel S Sign At The Elbow Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Clinical Examination Of The Musculoskeletal System




Carpal Compression Test Clinical Examination Of The Musculoskeletal System
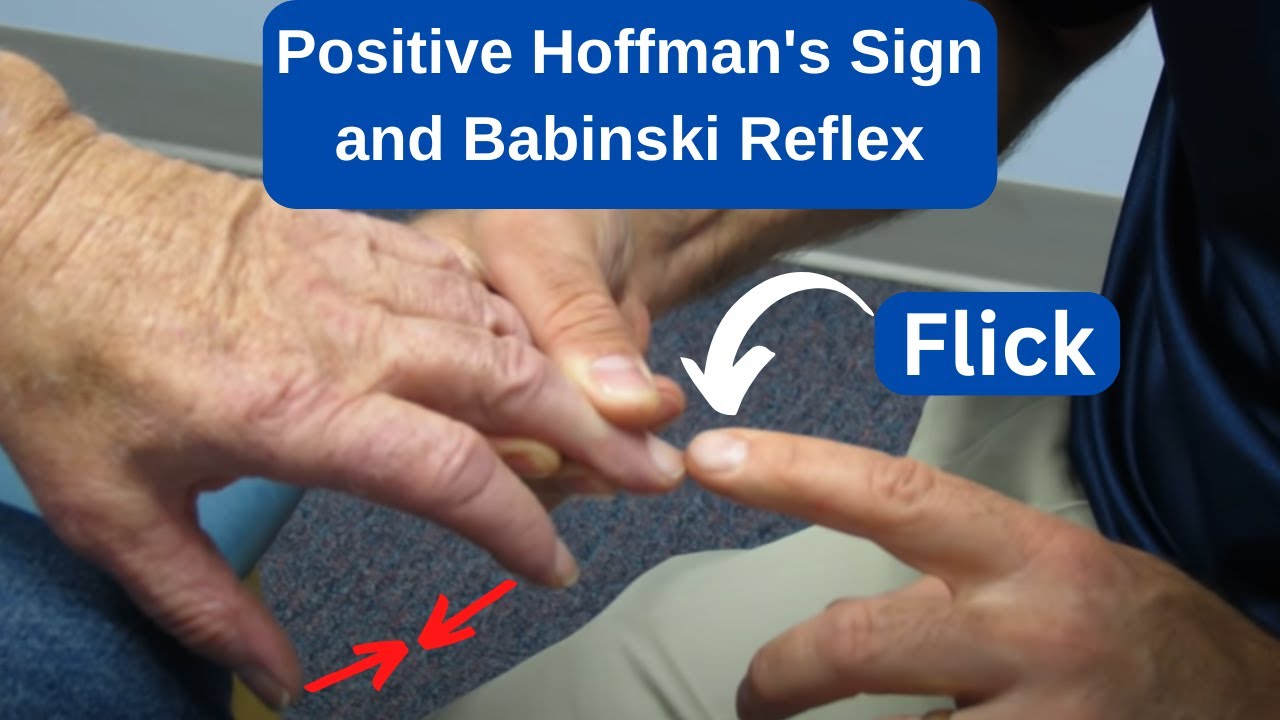



Hoffman S Sign Positive And Babinski Reflex In Ms Patient Youtube



1
/iStock_3573671_MEDIUM-582570425f9b58d5b178dd6f.jpg)



Strange Reflexes And What They Say About Your Health
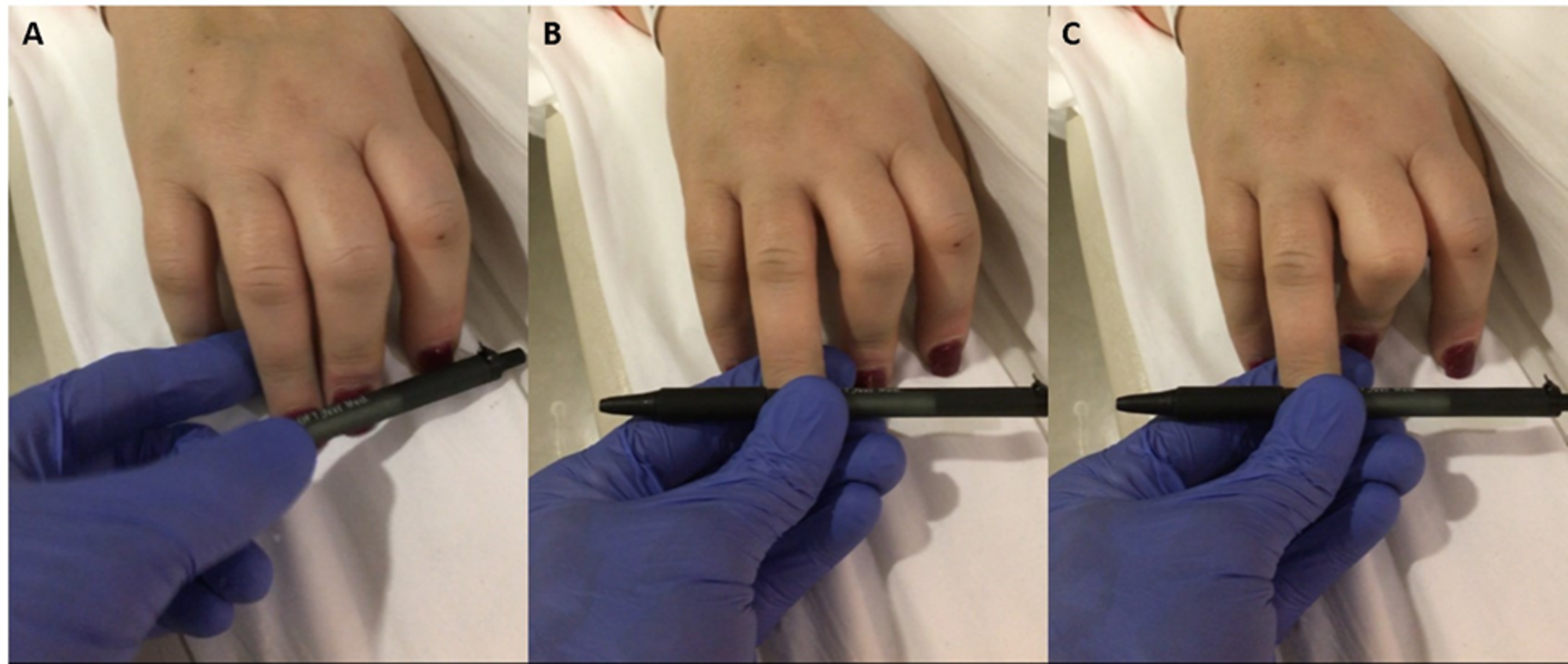



Cureus Finger Flexion To Noxious Stimulation In A Brain Dead Patient A Case Report And Review Of Literature




Neurological Signs In Medicine




What Is The Babinski Reflex




The Technique Used To Evoke The Hoffmann Reflex In Each Photograph Download Scientific Diagram
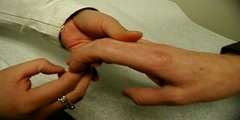



Hoffmann Sign Dnatube Com Scientific Video And Animation Site
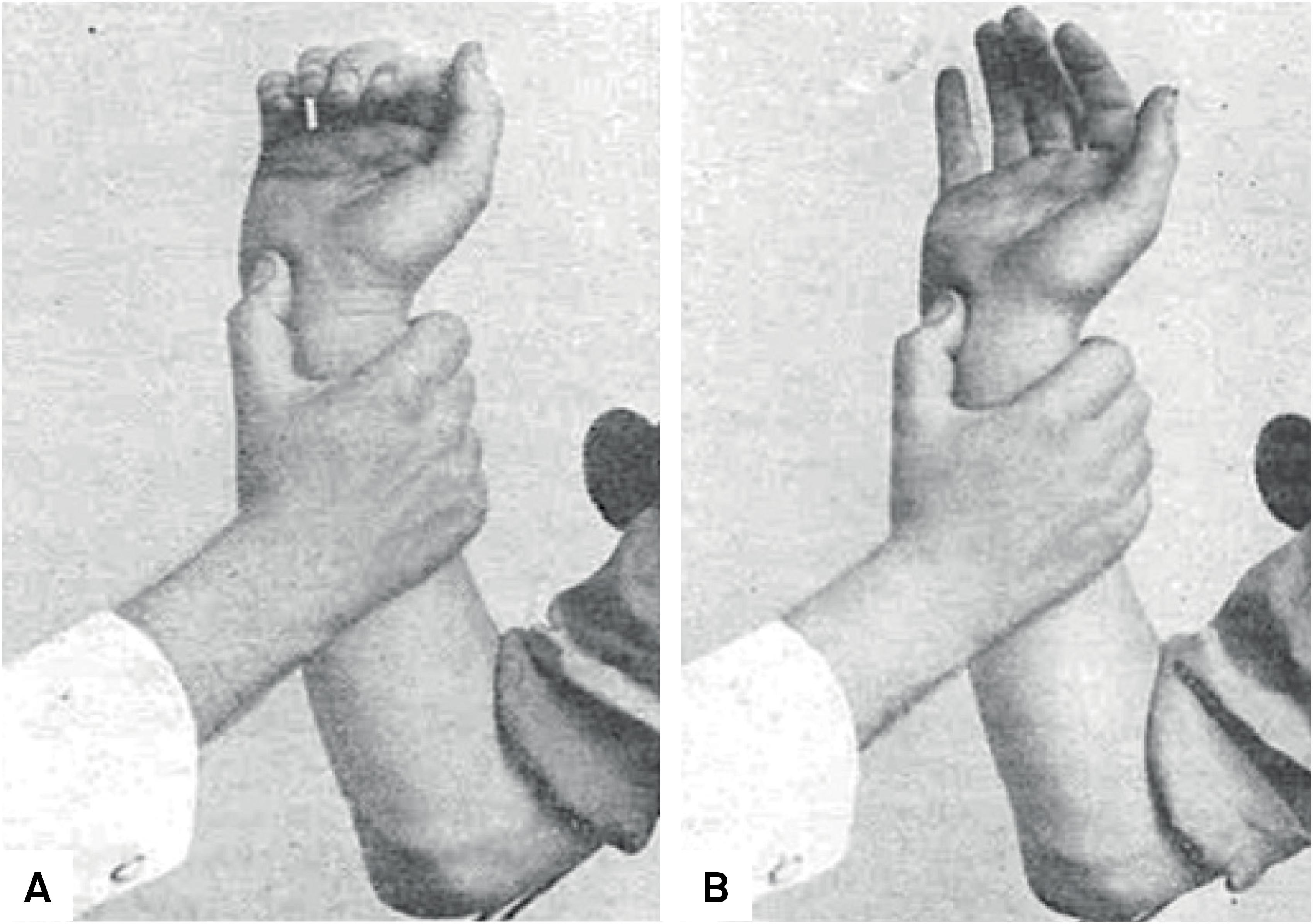



Scielo Brasil Babinski S Hand Sign Many Have Tried Babinski S Hand Sign Many Have Tried
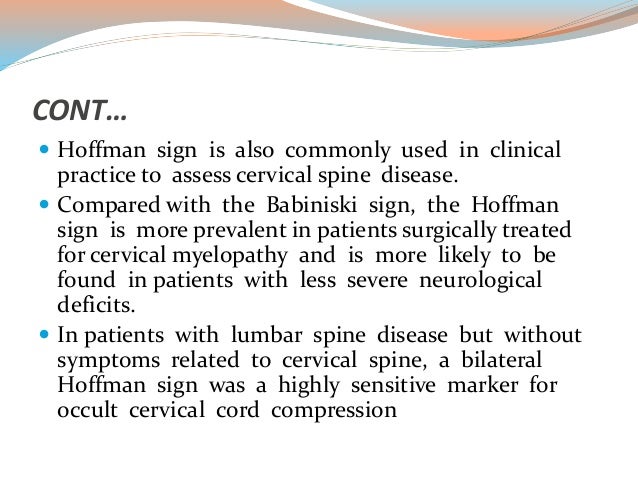



Neurological Signs In Medicine




Hoffmann Sign Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Orthostatic Hypotension As The Presenting Sign In Craniopharyngioma Neurology




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08 Journals



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿